Isotretinoin Guide: What You Need to Know Before Starting
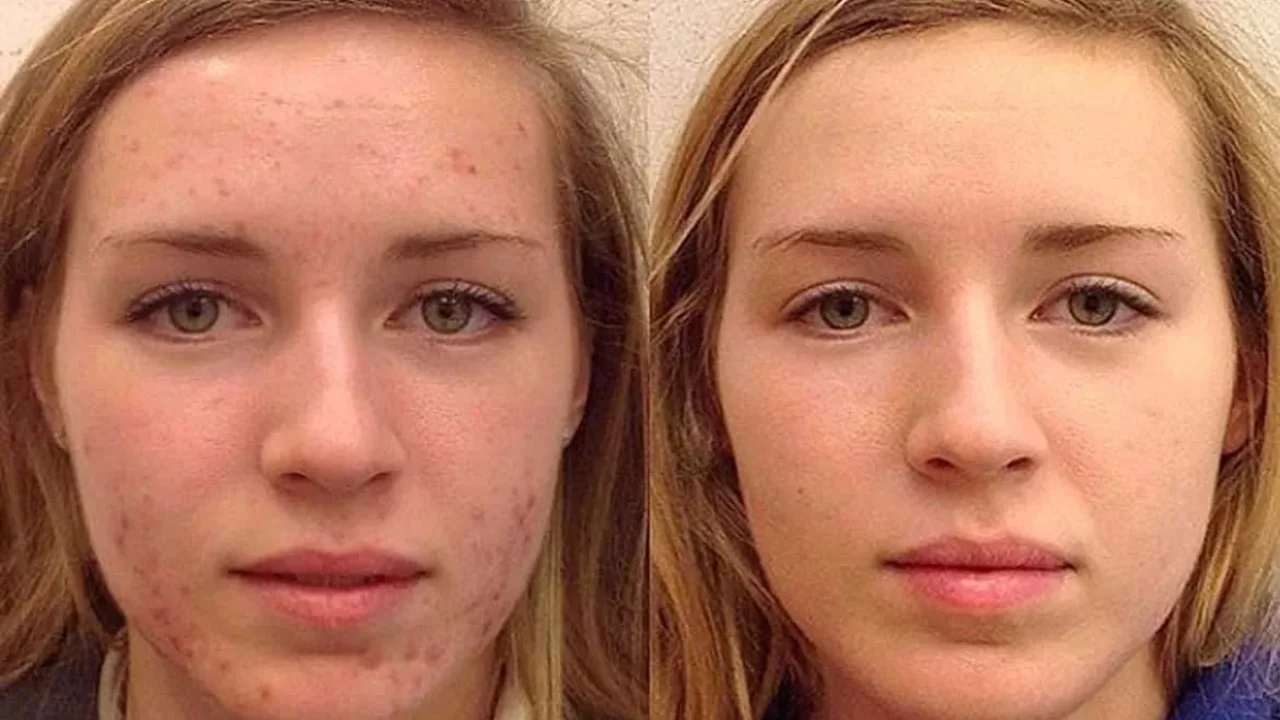
If you’ve tried creams, pills, and every home remedy without luck, you’ve probably heard doctors mention Isotretinoin. It’s the heavy‑duty oral retinoid that can clear stubborn cystic acne, but it’s not a casual over‑the‑counter product. Understanding how it works, what to expect, and how to stay safe can make the difference between a smooth finish and an unwanted side‑effect nightmare.
How Isotretinoin Works & Who Can Use It
Isotretinoin targets the four main causes of acne: excess oil, clogged pores, bacteria, and inflammation. By shrinking the sebaceous glands, it slashes oil production and helps skin shed dead cells more cleanly. Because of this power, doctors reserve it for severe nodular acne or cases that haven’t responded to other treatments.
Typical candidates are teens or adults with deep, painful breakouts that cause scarring. You’ll need a dermatologist’s prescription, and most clinics require a negative pregnancy test and a signed risk‑management agreement if you’re women of child‑bearing age.
Dosage, Side Effects, and Safety Tips
Doctors usually start with a dose of 0.5 mg per kilogram of body weight, taken once daily with food. Over a 4‑ to 6‑month course, the total dose often reaches 120‑150 mg/kg. This gradual approach helps the body adjust while still delivering strong acne control.
Common side effects include dry skin, chapped lips, and mild nosebleeds. Most people manage these with moisturizers and lip balms. More serious concerns—like joint aches, vision changes, or mood shifts—should prompt an immediate call to your doctor. Blood tests are routine every month to watch liver enzymes and triglyceride levels.
Pregnancy is a strict no‑go. Isotretinoin can cause severe birth defects, so reliable contraception is mandatory for at least a month before, during, and after treatment. Many clinics run a four‑step iPLEDGE program to track compliance.
While on Isotretinoin, stay hydrated, use gentle cleansers, and avoid aggressive exfoliants that can irritate dry skin. Sunscreen isn’t optional—your skin becomes more sensitive to UV rays, and sunburn can worsen long‑term pigmentation.
Don’t skip follow‑up appointments. Your dermatologist will tweak the dose based on how your skin reacts and the blood‑work results. If you notice any new or worsening symptoms, report them right away; early adjustments can keep the treatment on track.
After the course ends, many patients enjoy months of clear skin. Some doctors suggest a low‑dose maintenance pill to keep breakouts at bay, especially if acne flares up again. Talk to your provider about the best post‑treatment plan for you.
Bottom line: Isotretinoin can be a game‑changer for severe acne, but it requires commitment, monitoring, and a partnership with your dermatologist. Follow the dosage guide, watch for side effects, and keep those follow‑up visits—your skin will thank you in the long run.
Navigating the complexities of acne treatment can be challenging, especially when it comes to powerful medications like Isotretinoin, commonly known by its brand name Tretiva. This article delves into the essential aspects of safely ordering, using, and understanding Tretiva. It covers the medical benefits and side effects of Isotretinoin, common dosages and recommendations, and the significance of professional guidance. Whether you're considering Tretiva for your acne treatment or looking for trustworthy sources, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights.


 Medications
Medications




